INTRODUCTION
Enzyme kinetics is study of
the rates of enzyme-catalysed reactions. It’s principally concerned with the
measurement and mathematical description of this reaction rate and its
associated constants. To investigate the enzyme rates, Michaelis-Menten
equation (MM) is used. In this experiment, in order to discuss properties of an
enzyme (amylase), certain values are determined experimentally under steady
state conditions. These values are determined by using formula for kinetics
studies that include;
Vmax : The so-called maximal
rate of the catalysed reaction. The enzyme's active site is
saturated.
Km : The Michaelis constant.
The substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is one
half of its maximum value or also known as the turn over number.
half of its maximum value or also known as the turn over number.
These values are determined
experimentally by recording the progress of an enzyme-catalysed reaction using
fixed amount of enzyme and a series of different factors such as temperature, pH
and substrate concentration are test. These values used to construct a graph
that presenting the reaction rate occur. Different graph assemble different
reaction occur such as enzyme inhibition that act in varies of ways that affect
their kinetic effect.
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this experiment conduct was to determine the effect of substrate concentration, temperature and pH on enzyme activity. In this experiment we want to evaluate absorbance and the reaction rate of enzyme amylase in starch-iodine solution. The enzyme activity was measured through its absorption rate in the spectrophotometer with a wavelenght of 590 nm. To measure the result of each effects, we had plotted one standard reference graph from a 9 standard solution of starch (0, 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7 and 1.0 mg/ml) as a So. To test the effect of substrate concentration in enzyme activity, each standard solution was prepared in different concentration of water and amylase. Then, through the testing the enzyme at different temperatures and pH levels, it would determine at which temperature and pH level the enzyme worked the most efficiently. To test the optimal pH, the starch and a buffer were combined at a specific pH level and each sample was incubated for 10 minutes. For temperature, we used three different temperature of (8, 28, 40ºC) to determine the rate reaction of enzyme. Then, the solution was tested in spectrophotometer of 590 nm. Specific graphs were drawn to determine at which substrate concentration, pH and temperature was the optimum for the enzyme after the experiment. Through our result that we obtained, the enzyme amylase worked more efficiently under the pH level of 6 and 7. Michaelis- Menten kinetic theory proved that there is the relationship of substrate concentration to the reaction of the velocity.The lower the value of Km, the higher the affinity of the enzyme for enzyme substrate complex formation. For temperature, Enzyme reacts optimally at Vmax 0.01 where the affinity of the substrate is higher while the Km is lower, 0.005. However, since the whole testing experimental was taken only once, we cannot state that the results were precisely accurate
MATERIALS:
- Test tube
- Amylase
- Iodine
- Distilled water
- Waterbath
- Ice
- Spectrophotometer
PROCEDURES:
A)
Preparation of standard reference
- Starch solutions were prepared from the stock solution (1.0 mg/ml) into dilutions of 0.01, 0.025, 0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, and 1.0 mg/ml from the starch stock solution.
- Iodine solution is prepared by adding 5 g potassium iodide to 100 ml water. The dissolved potassium iodide is added with 1 g of iodine and is allowed to dissolve.
- A standard curve of Absorbance (@ 590 nm) vs Concentration of a starch/iodine mixture was prepared.
B) The
effect of substrate concentration.
- Standard starch solution was prepared into dilutions of 0.01, 0.025, 0.05,0.1, 0.3,0.5,0.7 and 1.0 mg/ml from the starch stock solution.
- The starch hydrolysis in different substrate concentration was prepared as the table below.
- Starch concentration was calculated after each sample undergoes hydrolysis by using standard curve. Starch concentration was calculated by using initial starch concentration and final starch concentration, [S]= (So) – (Sf)
- The velocity was calculated as V= ∆S/∆ t = (S0 – Sf) / 10 minutes
- By using the data collected, a Michaelis-Menten graph was plotted.
- The value of Vmax and Michelis constant Km were stated.
C)
The Effect of Temperature
- The following table below is uses as guide in an experiment the effect of temperature on enzyme.
- The Lineweaver-Burke line was plotted for the result of 20, 28, 35 and 40°C.
- All three plots in Lineweaver-Burke line were being compared.
- In the Lineweaver-Burke line, the values of Vmax and Km for all plots were find.
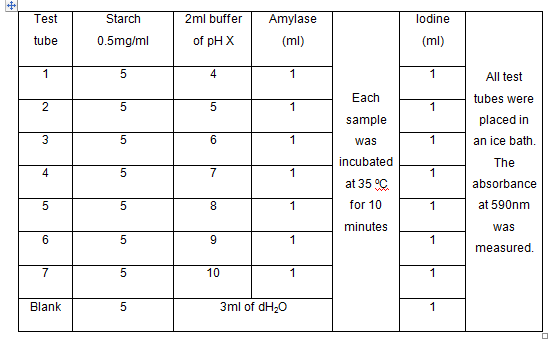
D) The
effect of pH
- The following table below is uses as guide in an experiment the effect of pH on enzyme
- The values of V for all pH were stated.
- The velocity for each pH test was compared.
RESULT AND DISCUSSION:
A) Standard Graph
B) The effect of Substrate Concentration
· Michaelis-Menten
graph is a graph that shows the relationship between the concentrations of a
substrate and the rate of the corresponding enzyme controlled reaction.
Michaelis-Menten kinetic theory of enzyme action state that enzyme
concentration and substrate concentration give effect on the velocity reaction.
The effect of enzyme concentration on reaction velocity means that if the
substrate concentration is held constant, the velocity of the reaction is
proportional to the enzyme concentration.
· In
this experiment, we are focusing on the second kinetic theory of enzyme action
which is the effect of substrate concentration on reaction velocity. There are
two orders that present in the Michaelis-Menten graph which are first order and
zero order. When the substrate concentration is low, the reaction velocity is
first order with respect to the substrate means that the reaction of velocity
is proportional to the substrate concentration. But, when the substrate
concentration becomes higher, the reaction velocity is zero order means that
velocity is independent of substrate concentration. At middle of substrate
concentration, the proportional of the reaction is changing.
·
There
are two parameters that involve in the Michaelis-Menten graph which is Vmax and
Km. Vmax is the maximum rate at which the enzyme can catalyze the reaction
while Km or Micahelis constant is the substrate concentration at half Vmax.
From the results, the maximum velocity is 0.062 and half Vmax is 0.031. Then,
Km was obtained from the graph at half Vmax and the value is 0.24. The
Michaelis constant,Km provide a measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its
substrate. The lower the value of Km, the higher the affinity of the enzyme for
enzyme substrate complex formation.
- For this experiment, we study about the relationship of activity of enzyme and temperature. Before explaining the graph, we should explain to you about the Vmax and Km that related to the enzyme activity calculations. Vmax refers to the velocity maximum that the enzyme can reach when certain temperature apply to a reaction, whereas, Km is Michealis constant, which shows us the affinity of an enzyme in a reaction. The lower Km readings the higher affinity of the enzyme
- In the calculation above, we can see that Vmax for temperature is 0.05. In a reaction the higher velocity the higher rate of reaction. This is because more collisions occur in between enzyme and substrate. As the temperature rises, molecular motion and hence collisions between enzyme and substrate speed up. But as enzymes are proteins, there is an upper limit beyond which the enzyme becomes denatured and ineffective.
- Km for 8oC is 0.42 , for 28oC is 0.4 whereas, for 40oC is 0.3. The type of inhibitor of the reaction is known as competitive inhibitor.
- The Km value is lower indicates that the enzyme have the higher affinity to react.
D) The Effect of pH
· Based
on the result obtained in Table 4, we can see that the highest velocity of the
enzyme reaction is at pH 6 and pH 7 which is 0.045 V. The velocity increased
rapidly from pH 5 to pH 6 at 0.003 V.
· Based
on Table 4, it shows that amylase used in this experiment is highly active at
pH 6 to pH 7. This can be shown by the static amount of velocity at both pH
values. The velocity decreased rapidly from pH 8 to pH 10. This shows that the
enzyme cannot react in those pHs. Thus, this shows that the enzyme can react
actively at pH below 7.
· In
the theory, it was stated that there are three types of amylase enzyme. The α-Amylase, β-Amylase, γ-Amylase enzyme.
· Each
types of amylase active optimally at different pH. The α-Amylase
react optimally at pH 6.7 to 7. The optimum pH for , β-Amylase is pH 4.0 to 5.0. While γ-Amylase optimally at pH 3.
· From
the result shown in Table 4, the enzyme reacts actively at pH 6 and pH 7. Therefore,
it is predicted that alpha amylase was used in this experiment.
· While
conducting the experiment, there are few error causes us failed to obtained the
exact result. One of the major errors occurs is the using of dropper
instead of micropipette. The function of the micropipette is to measure a small
reading of volume needed. In this experiment, the smallest volume used is 1 mL.
We used the dropper to measure and sometimes parallax error might occur during
the measurements thus giving the wrong reading for the volumes. Error in volume
of concentration might give the error for the absorbance reading. Thus it might
affect the result for the enzyme activity.
· During taken the measurement for the pH, we also used
the same of dropper and measuring cylinder. We might rinse both of dropper and
micropipette with not proper ways. This might contaminate the others pH
value.
CONCLUSION:
From these enzyme experiment, we can conclude that,
- In a nutshell, Michaelis- Menten kinetic theory proved that there is the relationship of substrate concentration to the reaction of the velocity.
- Enzyme reacts optimally at Vmax is 0.01. The affinity of the substrate is higher as the Km is lower which is 0.005.
- The enzyme, amylase reacts actively at pH 6 and pH 7.
REFERENCES:
· Donald B.Sittman, Victor L. Davidson (1999). BIOCHEMISTRY 4TH EDITION. Philadelphia : Lippincott-Raven Publisher.
·
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enzyme
·
http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/E/EnzymeKinetics.html
·
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Velocity
·
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amylase


















No comments:
Post a Comment